티스토리 뷰
반응형
1. 쉬프트 연산자 ( '>>', '<<')
public class SimpleTest {
@Test
void 쉬프트연산자와_일반_연산자_속도_테스트(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
long num = 1L;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
num = num<<1;
num = num>>1;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("*********************");
System.out.println((end-start)/1000.0);
System.out.println("*********************");
}
}
2. 일반 연산자를 했을 때
public class SimpleTest {
@Test
void 쉬프트연산자와_일반_연산자_속도_테스트(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
long num = 1L;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
num *=2;
num /=2;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("*********************");
System.out.println((end-start)/1000.0);
System.out.println("*********************");
}
}
3. 쉬프트 연산자를 쓰는 java.utils 클래스들
1. ArrayList
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = this.elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) {
if (this.elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(10, minCapacity);
} else if (minCapacity < 0) {
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
} else {
return minCapacity;
}
} else {
return newCapacity - 2147483639 <= 0 ? newCapacity : hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
}위의 메소드는 해당 사이즈가 일정 크기를 넘어서면 증가시키는 메소드인데 이 때 쉬프트 연산자를 쓰는 것을 볼 수가 있다.
그 이외에도
private static long[] nBits(int n) {
return new long[(n - 1 >> 6) + 1];
}
private static void setBit(long[] bits, int i) {
bits[i >> 6] |= 1L << i;
}
private static boolean isClear(long[] bits, int i) {
return (bits[i >> 6] & 1L << i) == 0L;
}기본적인 크기 증감에 대해서 쉬프트 연산자를 쓰고 있다.
2. PriorityQueue
private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es, int n) {
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable)x;
int child;
for(int half = n >>> 1; k < half; k = child) {
child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = es[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < n && ((Comparable)c).compareTo(es[right]) > 0) {
child = right;
c = es[right];
}
if (key.compareTo(c) <= 0) {
break;
}
es[k] = c;
}
es[k] = key;
}
해당 코드를 보면서 '>>>' 이건 뭐지? 하고 찾아본 결과 'unsigned shift operator'라고 한다.
일반적으로 (1 + Integer.MAX_VALUE )/2 를 하는 과정에서 오버 플로우가 발생한다.
하지만 '>>>'를 쓰면 그러한 걱정은 No No~~
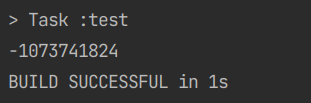
1. '>>'
public class SimpleTest {
@Test
void 쉬프트연산자_테스트(){
int one = 1;
int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println((1+max)>>1);
}
}
2. '>>>'
public class SimpleTest {
@Test
void 쉬프트연산자_테스트(){
int one = 1;
int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println((1+max)>>>1);
}
}
다른 것은 ArrayList와 비슷하게 구현되어 있다.
이렇게 쉬프트 연산자와 일반 연산자의 속도 차이에 대해서 알아보았다.
예전에 컬렉션에 있는 클래스에서 왜 쉬프트 연산자를 쓸까 생각을 했었는데 해당 속도 차이를 보고나니 무조건 쓸 수 밖에 없겠구나 하고 생각하게 되었다.
반응형
'JVM > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JAVA] Exception에 대하여 (0) | 2021.11.25 |
|---|---|
| [JAVA] 인터페이스에 대해서 (0) | 2021.11.20 |
| [JAVA] 클래스 변수를 잘 활용하라!(불필요한 객체 생성을 피하라) (0) | 2021.11.19 |
| [JAVA] 반복문, 조건문 놓치기 쉬운 것들 (0) | 2021.10.26 |
| [JAVA] '++' 와 '+=1' 의 속도 차이 (0) | 2021.10.22 |
반응형
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- 자바
- ubuntu
- headers
- 알고리즘
- docker
- env
- postgres
- 백준
- BFS
- Spring
- setattr
- dockerignore
- Celery
- 그래프
- docker-compose
- 파이썬
- Linux
- 카카오
- Python
- thread
- Collections
- PostgreSQL
- Command Line
- 프로그래머스
- DRF
- django
- 면접
- 2021 KAKAO BLIND RECRUITMENT
- Java
- Pattern
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
글 보관함
